SQL INNER JOIN
INNER JOIN
The INNER JOIN keyword selects records that have matching values in
both tables.
Let's look at a selection of the Products table:
| ProductID | ProductName | CategoryID | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chais | 1 | 18 |
| 2 | Chang | 1 | 19 |
| 3 | Aniseed Syrup | 2 | 10 |
And a selection of the Categories table:
| CategoryID | CategoryName | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Beverages | Soft drinks, coffees, teas, beers, and ales |
| 2 | Condiments | Sweet and savory sauces, relishes, spreads, and seasonings |
| 3 | Confections | Desserts, candies, and sweet breads |
We will join the Products table with the Categories table, by using the CategoryID field from both tables:
Example
Join Products and Categories with the INNER JOIN keyword:
SELECT ProductID, ProductName, CategoryName
FROM Products
INNER JOIN
Categories ON Products.CategoryID = Categories.CategoryID;
Try it Yourself »
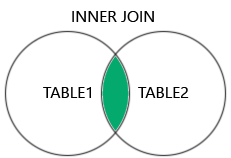
Note: The INNER JOIN keyword returns only rows with a match in both tables.
Which means that if you have a product with no CategoryID, or with a CategoryID that is not present in the Categories table, that record would not be returned in the result.
Syntax
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
Naming the Columns
It is a good practice to include the table name when specifying columns in the SQL statement.
Example
Specify the table names:
SELECT Products.ProductID, Products.ProductName, Categories.CategoryName
FROM Products
INNER JOIN Categories ON Products.CategoryID = Categories.CategoryID;
Try it Yourself »
The example above works without specifying table names, because none of the
specified column names are present in both tables.
If you try to include CategoryID in the
SELECT statement, you will get an error if you do not specify the table name
(because CategoryID is present in both tables).
JOIN or INNER JOIN
JOIN and INNER JOIN will return the same result.
INNER is the default join type for JOIN,
so when you write JOIN the parser actually writes INNER JOIN.
Example
JOIN is the same as INNER JOIN:
SELECT Products.ProductID, Products.ProductName, Categories.CategoryName
FROM Products
JOIN Categories ON Products.CategoryID = Categories.CategoryID;
Try it Yourself »
JOIN Three Tables
The following SQL statement selects all orders with customer and shipper information:
Example
SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CustomerName, Shippers.ShipperName
FROM
((Orders
INNER JOIN Customers ON Orders.CustomerID = Customers.CustomerID)
INNER JOIN Shippers ON Orders.ShipperID = Shippers.ShipperID);
Try it Yourself »